For good food product, personal hygiene rules must be established, because neglecting personal hygiene leads to contamination of the product and cause consumer diseases, which is reflected in the reputation of the facility
Personal hygiene components (hair, protective clothing, smoking, hands, accessories and perfumes) Division of production areas
The role of quality assurance in controlling personal hygiene rules
Table of Contents
personal hygiene elements:

Hair:
Hair carries dust and pathogenic bacteria If it reaches food, either through hair loss or dust and dandruff – which carries with it Staphylococcus bacteria – for food or pharmaceutical products. Therefore, it is prevented from appearing beard and mustache, and covering the hair completely with a head covering, a mask for the mustache, and a cap. Hands completely
Protective clothing: It must meet the following conditions for personal hygiene
Light in color and covers the personal clothing completely, covering the entire body
It is prohibited to have pockets, buttons, or zippers (use snap buttons).
Protective clothing Is to protect the product from contamination of a product with special clothing or the transfer of something from the worker to the product.
It is made of fabric that can be washed daily and sterilized, and swabs are taken to culture them bacterially according to a timetable determined by quality assurance.
Special shoes must be worn in a dry area and always cleaned.
Work clothes are worn within designated areas close to the work area, taking into account the placement of two doors between the changing areas and the production area
Hands:
Hands are an essential factor for the transfer of microbes to products (food – medicine). Therefore, quality assurance must impose rules for washing and sterilizing hands, train workers on them, and monitor the quality of washing through bacterial hand swabs according to a timetable determined by quality assurance.
When and how do we wash our hands?
Before starting work – before wearing sterile clothing and paws – after touching waste or waste bins – after sneezing and coughing – after touching raw and cooked food – after using the toilet – after smoking
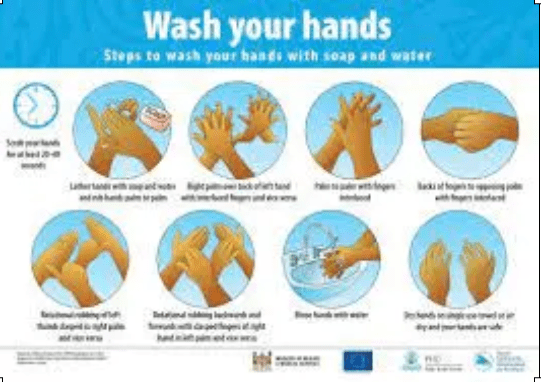
- Wash with warm water at a temperature of 30-35 degrees Celsius using the following steps:
- Wet hands well with water, then add the appropriate soap (preferably without smell).
- Rub the palms and between the fingers for 20 seconds
- Rub the backs of the fingers well and the thumbs toward the palms
- Clean under the nails In a circular motion with the palm of the other hand
- Wash hands well with soap
- Use a single-use paper towel to dry and dispose of it in containers that open by pressing with the foot
- Disinfect hands with conventional disinfectants (65%-80% alcohol).
Washing areas near manufacturing areas and the distribution of laundries must be designed to suit the number of workers according to the following:
- Smoking: Smoking Is strictly prohibited in workplaces, manufacturing areas, or surrounding buildings, for the following reasons:
- Cigarette ash getting into the product or food
- Throwing cigarette butts loaded with bacteria-rich saliva in production areas
- Cigarette smoke reaches the product, In addition to causing coughing or sneezing among the rest of the workers, thus causing saliva to reach the products
- Jewelry (accessories) and perfumes: It is strictly prohibited to wear all types of jewelry (rings – bracelets – necklaces…) because they carry dust and it is possible that parts of them will fall Into the food or product during manufacturing.
Perfumes: They directly affect the taste of the product, in addition to causing sneezing and the access of saliva and pathogenic bacteria to the products.
Division of production areas (manufacturing)to got personal hygiene:
The degree of health requirements varies according to the sensitivity of the manufacturing area, depending on the sensitivity of the product and its susceptibility to germs
What is the difference between cleaning, disinfection, and sterilization?
- Cleaning: Removing dirt or unwanted residue with soap and water or water and chemical detergents
- Disinfection: Eliminating pathogenic germs in all their forms without getting rid of their spores with hot water and disinfectants in studied concentrations or exposure to heat at 85 degrees Celsius for 10 minutes.
- Sterilization: Getting rid of all pathogenic and non-pathogenic germs and their spores using disinfectants and heat at 120 degrees Celsius.
Therefore, production areas are divided according to the degree of sterilization, disinfection, and sterilization
Controlling these areas Is one of the basic tasks of quality assurance management
What are the tasks of quality assurance in controlling health requirements to personal hygiene?

- Placing information boards with hand washing instructions
- Dividing production areas and training workers on the appropriate clothing for each production area and methods of cleaning, disinfection and sterilization for each area.
Determine, control and monitor the rest area and its special times
Conduct periodic bacterial swabs on workers’ clothing and hands to ensure the effectiveness of the established requirements
Develop a cleaning, disinfection and sterilization program for all departments and directly supervise its implementation
Read more:

